The term of study for the Master’s Degree for full-time education is 2 years, or four semesters. The modules for semesters are distributed in such a way that student can first form an idea about the main issues of modern architecture, problems and methods of scientific research through lecture courses. After that, in the second semester the adjacent departments, the material is refined, which allows the student to independently choose the spectrum of subjects required for his research (module of variable subjects) in the third semester. The fourth semester is 80% self-study. At this stage, student’s work is approaching it’s completion and a large amount of independent studies allows student to focus on the final results and defend the thesis successfully.
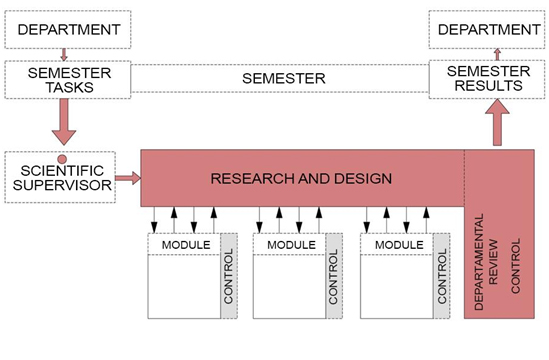
2016 MARKHI Master’s Degree Program switched to a modular training system. A qualitative difference of the new system is the coordinating roles of the specialised departments and of the supervisor of the thesis (Fig. 2). This allowed to form the entire training program according to the student’s chosen research theme and created a favorable atmosphere for scientific and creative search. MARKHI Master’s program supports an individual approach in the education of every student. The subjects that form the modules are given through intensive courses of 6-8 weeks, which ensure the effectiveness of mastering the material.
There are two ongoing disciplines during the two years of training:
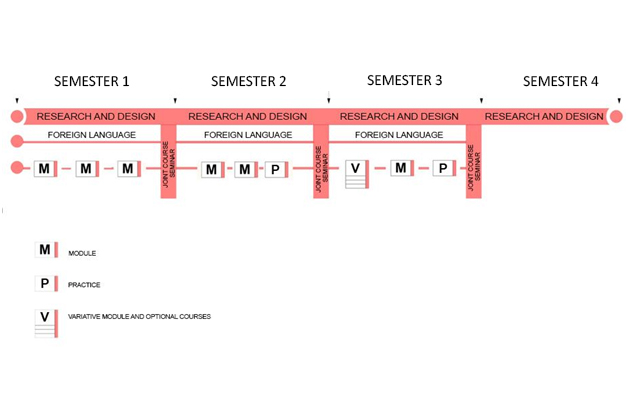
” Research and Design” – departamental classes that directly provide the student’s specialisation and are focused on work on the thesis research and experimental project. (Fig. 1)
Foreign language, as an obligatory discipline in the preparation of an educated modern professional. (Fig. 1)
All other subjects are divided into modules according to semesters.
Year 1
First semester
First Module. Theoretical block, contributing to the determination of the student’s thesis problem, and introducing the students to the course of trends in the development of modern architecture, the latest scientific research. This Module includes following disciplines:
– Actual Problems of History and Theory of Architecture
– Aesthetics of Design Solution
– Theory of Town Planning and Scientific Methods of Research
The second module includes subjects determined to build students’ research skills:
– Russian Language. Scientific style
– Foreign Language. Intensive program
– Architectural scientific research
Third module. Mastering the skills of practical implementation, generalisation and systematisation of the studied material:
– Principles of Geographic Information System and Instruments of Urban Context Analysis
– Digital Parametric Means of Architectural Formation
– Contemporary Methodology of Architectural Analysis
Second semester.
The second semester consists of 3 modules: two blocks of subjects and one module of practice.
The first module is providing the hypothesis of scientific research with practical knowledge of the possibilities of modern designs, engineering equipment, building materials. It includes disciplines:
– Architectural and Construction Materials
– Architectural and Building Constructions and Technologies
– Engineering systems and Environment
– Modern methods of Buildings’ Erection
The second module. In the framework of this module, the student must learn the legal provision of the architectural profession. This module ends with practice in the architectural bureau so that the student can learn the practical implementation of the theoretical material. The module includes disciplines:
– Legal Aspects of Architectural Activity
– Architectural Project Management
– Architectural Management
– Economics of Architectural Project
Third semester
The first module. Current module refines and specifies the Master’s Thesis. It consists of a list of highly specialized selective subjects:
– Ecology
– Landscape Architecture
– Resource Saving Technologies
– Sociology of Architectural and Town Planning Solutions
– Cadastre
– Architectural Physics
– Constructions
– High-rise buildings’ Erection
– Economics of Project Solutions
– Reconstruction and Restoration of Historical Town.
The student must choose three subjects from the list above.
The second module is a representative module, it includes subjects that can help students defend their Master’s Thesis. It also includes the necessary preparation of reports and presentations, including the reports for the annual MARKHI International Scientific and Practical Conference. This module contributes to the development of communication skills and ability to hold a discussion. The module includes following subjects:
– Project Presentation
– Architectural Pedagogics
– Final Portfolio
– Business Ethics
The module ends with Teaching Practice.
Fourth semester
The fourth semester is devoted entirely to the work of the student with the scientific supervisor and related departments and specialists with the field of expertise that corresponds to the student’s Master’s Thesis. As part of the Practical Training, the student must independently apply the skills obtained during 3 semesters of training. The result is the Master’s Thesis.
The approximate volume of the Master’s Thesis without the annexes is 40-80 pages.
The Thesis should contain:
- The cover and a title page of the Master’s Thesis, signed by the student, the scientific supervisor and the head of the Master’s programmes of the department, and also by at least two consultants on the sections of experimental design;
- Contents (Table of contents);
- Abstract (1-2 pages);
- Introduction (1-2 pages);
- The main part, consisting of 2-4 chapters, including the following mandatory provisions:
– analysis of the scientific problem;
– study of researches carried out in this field earlier;
– the construction of theoretical models, the statement of the main provisions of the scientific concept;
– design problem analysis based on analogs;
– project situation analysis;
– explanatory note on the project and technical and economic indicators;
– comparison of the obtained results with the research theoretical model and the analysis of the obtained results;
- Conclusion, including the main findings of the Master’s Thesis;
- References;
- Annexes.
Abstract of the Thesis. Size A5
Abstract cover sheet.
Cover sheet – the first page of the abstract with a stamp “On the Manuscript Rights.”
The reverse side of the cover of the author’s abstract with a sign that protects the copyright of the student.
General description of Thesis
The introductory section begins with identifying the relevance (1 page). Part of the relevance is a brief review of the literature, which should lead to the idea that the current topic is not adequately disclosed and requires scientific and project comprehension and development (1 page). The main theme of the research is formulated based on the conclusions made in the literature review. The introductory part is made in the following order:
– aims and objectives;
– object and subject of the research;
– methodology and methods of research;
– scientific novelty of the work in the form of basic provisions;
– practical value;
– the boundaries of the study;
– research hypothesis;
– the section “To be defended”;
– approbation of work;
– size and structure of the dissertation.
Contents and main items of the thesis
The section begins with the general description of the thesis, for example: “The introduction substantiates the relevance of the topic, reveals the level of elaboration of the question, and determines the goals, tasks, methods, object, subject and boundaries of research, it’s scientific novelty and practical value.”
After that, each chapter is described separately. The title of the chapter is either in capital letters or in bold.
The presentation of the material should be concise and accurate. It is necessary to avoid complex syntax constructions and use of “slang”. Terms and words can be replaced by abbreviations and accepted text abbreviations, but they should not be particularly abused. Reduction of the abstract size made by reduction of the number of arguments, comparisons, justifications, descriptions, etc.
Main results and conclusions of the research
This section is a generalization of the matters researched in the Master’s Thesis. This is not just a list of results, but their synthesis, that is the actual new material that the student has contributed to the research of the problem. The main results and conclusions should be numbered, there should be no more than ten.
The main publications on the topic of the Thesis
– Graphic exposition
The exposition part is 6 to 8 panels 1m x 2m, executed at a high professional level, should include the design and scientific parts of the study.
| For Design Master:
|
For Research Master:
|
| It is recommended to begin and complete the exposition with a scientific part, and use graphic drawings (designs) proving the competence of the thesis in the center as a demonstrative basis.
The design part may consist (by the decision of the department): – 4-6 panels 1×2 meters, dedicated to one design solution. In this case, the design should be highly detailed.
– 4-6 panels 1×2 meters, dedicated to 4 different projects, connected by a single idea or responding to different aspects of one issue raised in the thesis. The number of such “mini-projects” can be decided by the department.
Depending on the research subject, the number of experimental projects can be reduced while maintaining the total size of the graphic part (6 panels 1m x 2m) with mandatory coordination with the departmental committee.
The design project can represent both an integral object and its fragment depending on the research (for example, a fragment of an urban environment or a fragment of interior spaces). The choice of necessary projections, working models, and their number is justified by the specific tasks of the research. Design projects must be completed as fully-developed buildings (including all plans, facades and sections). Experimental half semester design projects should confirm the reliability of the theoretical research findings, idea concepts and new modern solutions of old problems. Therefore, the design area can include parts of buildings, groups of premises, fragments of quarters, squares. The depth of elaboration must prove the possibility of realizing the idea laid down in the theoretical part of the work. It is assumed that for a competent and modern solution to a particular problem it is necessary to involve information from related fields of knowledge and sciences with the aim of achieving a quality of residential or public space
|
A similar scheme is recommended for placing panels and their number. However, instead of a design solution or solutions, it is necessary to form an evidence base by providing generalized schemes, typologies, basic principles. |
– design models (depending on the research topic and at the request of the department)
– 2 publications
-2 reviews (one external, including the expert tutor of the MARKHI department, and one internal (from the department, where the supervisor is working, or the one where the student is trained (attached)).
Modern Master’s degree research should be oriented towards ensuring the human existential needs from the point of view of human values such as “environment”, “spirit of the place”, “human scale”, “authenticity”, “identity”, considering new technologies and resource-saving systems.
Theoretical research should end with the development of an architectural (theoretical) concept and scientifically substantiated conclusions that have signs of novelty in the obtained results.
Practical research should end with the development of an architectural concept (design project) based on the analysis and assuming the actualization of contemporary problems of architectural development in design proposals.
The themes for Master’s Thesis are determined by the department and the student, taking into account the latest trends in architecture and the latest technologies. The themes that were determined in 2016 can be conditionally divided into 4 groups;
- Reconstruction, regeneration of industrial and urban areas, residential quarters and public spaces.
- Urban planning landscapes. Morphology of urban neighborhoods and public spaces.
- Application of modern architectural technologies in the design of objects in different climatic and geographical conditions.
- Modern theoretical problems of architectural research.
Students will need to make design decisions related to the selected topics within the subject “Research and design” during the two years of training. These decisions should be the design evidence base for the master’s thesis.
There are 11 departments accepting students with the speciality ARCHITECTURE:
Architecture of Residential Buildings
Architecture of Public Buildings
Architecture of Industrial Buildings and Constructions
Architecture of Rural Settlements
Landscape Architecture
Restoration of Architectural Monuments
Architectural Reconstruction
Theory and History of Architecture
Soviet and Modern Foreign Architecture
Temple Architecture
Urban Design
The Master’s Degree Program of MARCHI is closely connected with the Union of Moscow Architects, one of the MARKHI departments – “Integrated professional training”, is established on the basis of the Union. This allowed creating a unique course of lectures by modern architects and related specialists, namely BIM-technologies. MARKHI Master’s level students have the opportunity to practice at the leading architectural bureaus of Moscow.
The students’ schedule is drawn up in such a way that for two days the master student is engaged in practical work on the thesis (within the subject “Research and Design”), two days are given to theoretical and related subjects and two days are left for the student’s independent work.
It should be noted that the main educational training programs were highly appreciated by representatives of the professional community.
The Master’s Degree Programme ends with the State Final Examination where the student presents of the report on the received competences to State Examination Board. The commission of the invited architects, scientists and professors of a high-rank reviews student’s research work and the design project which is executed on the basis of a research work and shows the conclusions of this work.
The student submits the text of research work, the abstract, publications of scientific articles on a subject of the research and an exposition of a graphic part with explanations on the research subject. The design project is included in the general exposition.
Also State Examination Board considers the review of the research work written by the candidate of architecture and the explanatory note to the design project signed by tutors of disciplines adjacent to design studio. Also, the abstract of the research work in Russian and English languages is submitted to the commission.
The student presents the report on the work in which he/she covers a theoretical part of a research and comments on the design project, answers questions of the commission members. In the course of protection of the work, the student shows all competences formed during the 2-year training. The Commission hears the supervisor’s comment on the student and the educational skills that student received. Then members of the commission discuss the work in the form of personal reports. After the defense and approval of all members of the commission, the commission chairman announces the decision to assign master’s degree qualification to the student or explains the reasons for refusal. At the end of the session, the commission estimates students’ works according to the 5 point scale. Points are given by all members of the commission.

